Literature Sharing | ECE-CYC1 Transcription Factor CmCYC1a May Interact withCmCYC2 in Regulating Flower Symmetry and Stamen Development in Chrysanthemum morifolium
Release time:
2025-06-17
This study investigates the role of CmCYC1a, a CYC1 subclade gene from the ECE (CYC/TB1) family, in the floral development of Chrysanthemum morifolium. The gene was found to be more highly expressed in disc florets than in ray florets, with expression increasing during the flowering process. Functional analysis through overexpression in Arabidopsis thaliana revealed that CmCYC1a can alter floral symmetry from actinomorphic to zygomorphic and reduce the number of stamens. Additionally, yeast two-hybrid assays showed that CmCYC1a interacts with CmCYC2b, CmCYC2d, and CmCYC2f. These findings suggest that CmCYC1a contributes to the regulation of flower symmetry and stamen development in Chrysanthemum morifolium, and, together with CYC2 genes, may play a coordinated role in capitulum formation, providing new insights into the function of ECE genes in Asteraceae.
CmCYC1a, a 1095 bp coding sequence isolated from the inflorescences of the chrysanthemum cultivar 'Fen Ditan', encodes a 364-amino acid protein. Phylogenetic analysis confirmed that CmCYC1a belongs to the CYC1 subclade and is closely related to CYC1 genes from Gerbera hybrida and Helianthus annuus. Sequence alignment showed that CmCYC1a contains a conserved TCP domain, an arginine-rich R domain, and a complete ECE motif, characteristic features of ECE family proteins.
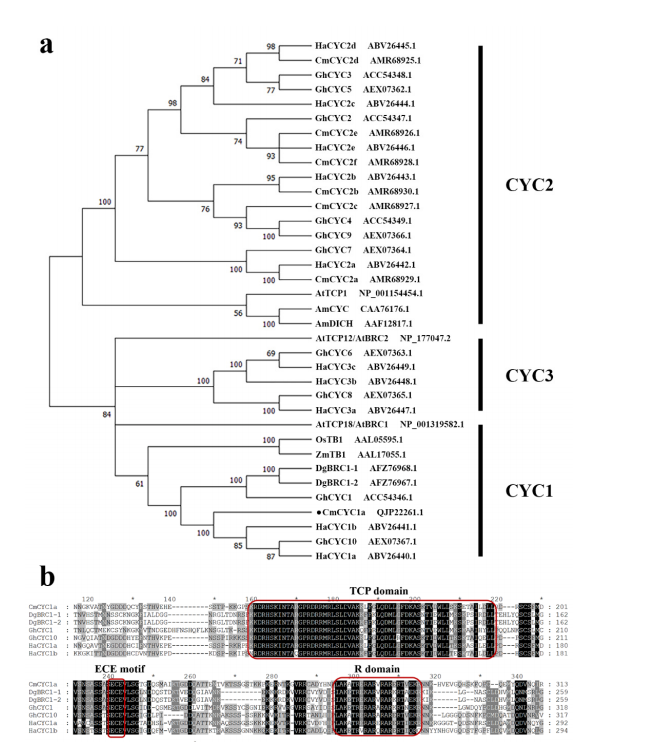
Figure 1. Phylogenetic analysis and sequence alignment of CmCYC1a.
qPCR analysis revealed that CmCYC1a is expressed at higher levels in disc florets than in ray florets, with expression gradually increasing during flower development and peaking at stage 5. At later flowering stages, CmCYC1a was detected in all floral organs, showing higher expression in involucral bracts and receptacles, and higher levels in disc petals compared to ray petals.
To investigate the role of CmCYC1a in flower development, the gene was ectopically expressed in Arabidopsis. Three transgenic lines were confirmed and analyzed, showing a shift in floral symmetry from polysymmetric to monosymmetric and a reduction in stamen number from six to four or five. These findings suggest that CmCYC1a plays a role in regulating flower symmetry and stamen development.
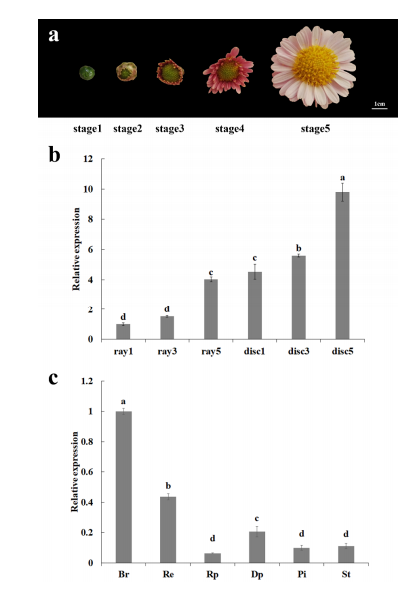
Figure 2. Expression analysis of CmCYC1a in C. morifolium ‘Fen Ditan’ during flowering process.
Overexpression of CmCYC1a in Arabidopsis changed flower symmetry from polysymmetric to monosymmetric and reduced the number of stamens from six to four or five, demonstrating its role in regulating flower symmetry and stamen development.
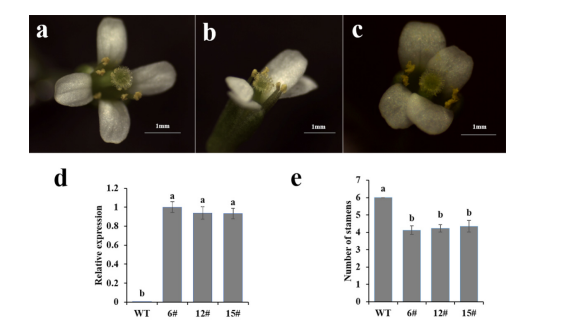
Figure 3. Ectopic expression of CmCYC1a in Arabidopsis.
CmCYC1a localizes mainly in the nucleus, similar to CmCYC2. Yeast two-hybrid assays showed that CmCYC1a strongly interacts with CmCYC2d and CmCYC2f, and weakly with CmCYC2b. These results suggest three protein–protein interaction pairs: CmCYC1a with CmCYC2b, CmCYC2d, and CmCYC2f.
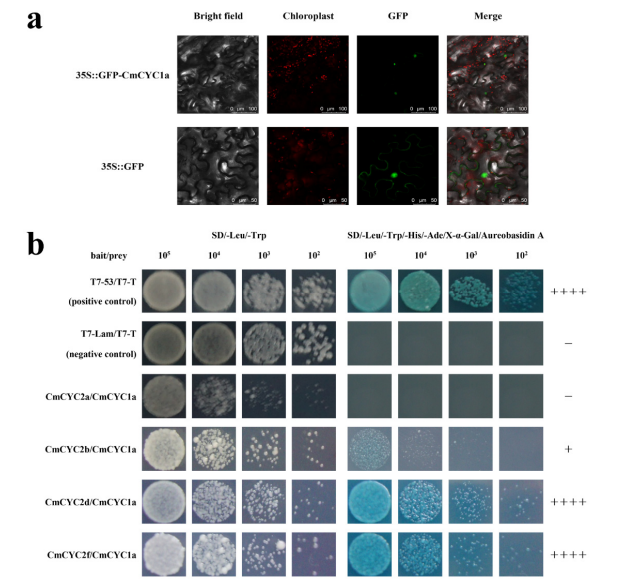
Figure 4. Interactions between CmCYC1a and CmCYC2
This study isolated and characterized the ECE-CYC1 gene CmCYC1a in Chrysanthemum morifolium, finding it expressed more in disc florets and increasing during flower development. Overexpression of CmCYC1a in Arabidopsis altered flower symmetry to zygomorphic and reduced stamen number, similar to CmCYC2 gene effects. Yeast two-hybrid assays showed CmCYC1a interacts with CmCYC2b, CmCYC2d, and CmCYC2f. The results suggest that CmCYC1a and CmCYC2 have partially redundant roles and cooperate via protein interactions in regulating flower symmetry and stamen development during capitulum formation. These findings advance understanding of chrysanthemum inflorescence molecular mechanisms and the role of ECE genes in flower morphology.
Related News
2025-06-17
2025-06-12
2025-06-10
2025-06-06
Literature Sharing | SPL1 positively regulates cuticular ridge wax biosynthesis in Arabidopsis
2025-06-04
Functional study of plant hormone transporters using a heterologous system
2025-05-29
2025-05-27
2025-05-22