Services
Providing Advanced Biological Technical Services for Researchers in Fundamental Science
Plant Genetic Transformation Services
High-Efficiency Genetic Engineering Solutions for Multiple Plant Species
Service Overview
Plant genetic transformation refers to the process of introducing foreign genes or plasmids into plant cells and integrating them into the plant genome. This technique is not only fundamental for studying plant development and gene function, but also essential in modern agriculture for breeding crops with improved traits.
We offer comprehensive genetic modification services—such as gene knockout, overexpression, and precise editing (PE)—across a wide range of species, including:
Model plants: Arabidopsis thaliana, tobacco, rice
Major crops: maize, potato, soybean
Economic plants: tomato, lettuce
Forage grasses: Cynodon dactylon, Poa pratensis, Agrostis stolonifera, Zoysia japonica
Our advanced and stable transformation systems help introduce desirable traits like yield improvement, enhanced nutrition, and stress resistance. Services are fully customizable, covering project design, feasibility evaluation, execution, and training support.
Workflow
Species and vector selection
Gene synthesis and vector construction
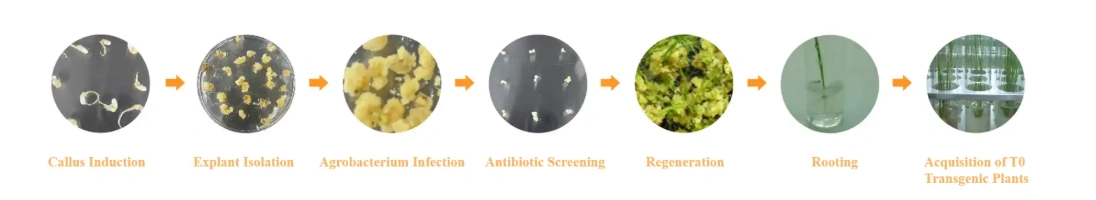
Tissue preparation and transformation
Resistant callus screening and regeneration
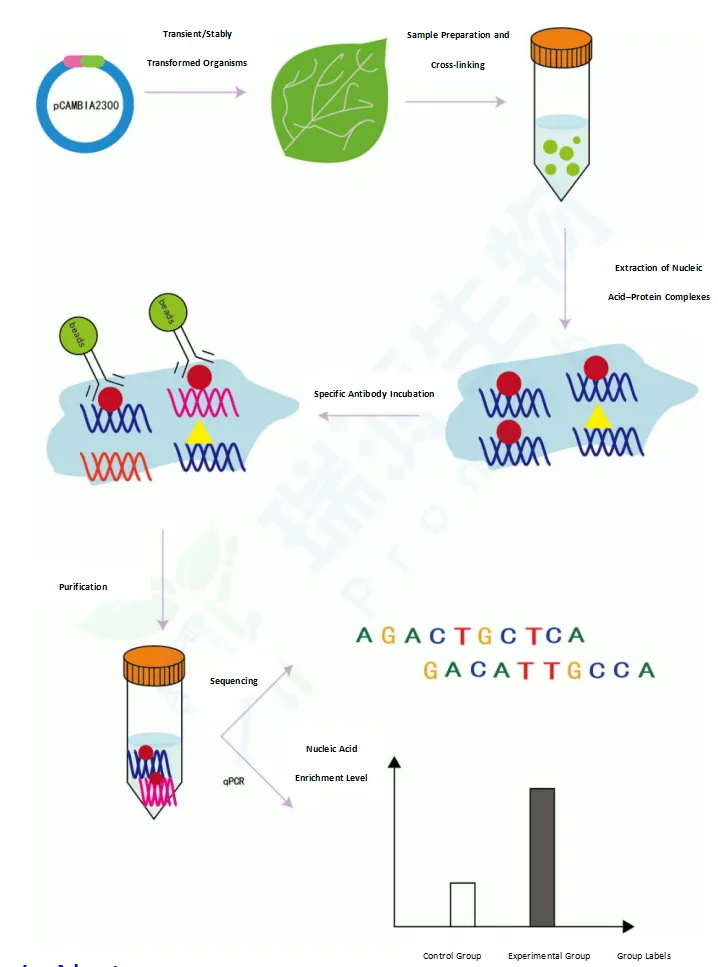
PCR/Sanger sequencing for positive T0 lines
(Optional) Gene expression verification via qPCR
Technical Advantages
Tailored Solutions: Multidimensional services—overexpression, RNAi, CRISPR editing—with customizable strategies in vector construction, transformation, detection, and analysis.
Wide Species Coverage: Applicable to rice, soybean, maize, tomato, lettuce, tobacco, Arabidopsis, potato, and more.
Efficient Screening: Supports various eukaryotic resistance markers (Hygromycin, G418, Basta, Glyphosate, Mannose); offers PCR and Sanger sequencing reports for resistant lines.
Full Project Support: Expert pre-sale consultation, detailed project design, transparent experiment tracking, and comprehensive final reports.
Experimental Workflow & Deliverables
Service | Delivery materials |
A. Selection of target genes B. Gene synthesis / Vector construction | The transformed plasmid vector |
A. Preparation of explants B. Infection of explants C. Callus selection D. Callus differentiation into shoots | T0 positive seedlings |
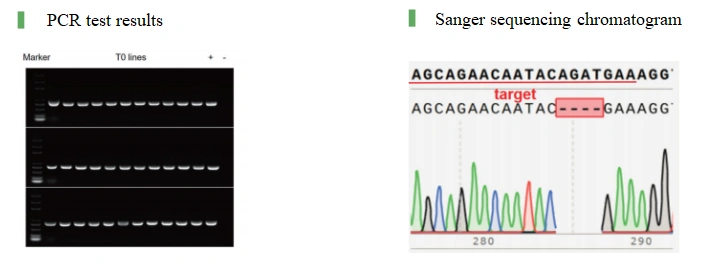
A. DNA extraction C.PCR amplification and gel electrophoresis D. Sanger sequencing | 1. PCR detection report 2. Sanger sequencing chromatogram |
A. RNA extraction (optional) B. qPCR primer design C. Real-time PCR D. Quantitative data analysis | 1. Raw data and result images 2.Standard experimental report (including experimental steps and workflow) |
Supported Species, Services, and Timeline
Species | Service type | Variety | Service period | Delivery standards |
Rice | Genetic transformation | Japonica rice varieties such as Nipponbare and Zhonghua 11 | 2.5 to 3 months | At least 20 PCR-positive T0 plants |
Single-gene knockout | At least 10 T0 edited lines | |||
Multi-gene knockout | At least 10 T0 edited lines | |||
Genetic transformation | Indica rice varieties such as Huanghuazhan and Meixiangzhan | 4 to 5 months | At least 10 PCR-positive T0 plants | |
Single-gene knockout | At least 5 T0 edited lines | |||
Multi-gene knockout | At least 5 T0 edited lines | |||
Forage grasses (Bermudagrass, Kentucky bluegrass, Creeping bentgrass, Zoysiagrass) | Genetic transformation | Baron,Common,Tiger, Companion | 6 to 8 months | At least 5 T0 plants |
Single-gene knockout | At least 5 T0 edited lines | |||
Multi-gene knockout | At least 5 T0 edited lines | |||
Soybean | Genetic transformation | Soybean varieties such as W82, Jack, Zhonghuang 302, and Jiyu 86 | 4 to 5 months | At least 15 positive T0 plants |
Single-gene knockout | 5 to 6 months | At least 5 T0 edited lines | ||
Multi-gene knockout | 5 to 6 months | At least 5 T0 edited lines | ||
Precision Editing (PE) | 7 to 8 months | At least 3 T0 edited lines | ||
Maize | Genetic transformation | Research maize varieties such as B104, KN5585, and B73 | 8 to 10 months | At least 10 batches of T1 generation Bar test strip–positive seeds |
Single-gene knockout | 8 to 10 months | At least 5 batches of T1 generation edited seeds | ||
Multi-gene knockout | 8 to 10 months | At least 5 batches of T1 generation edited seeds | ||
Precision Editing (PE) | 10 to 12 months | At least 3 T0 generation edited lines | ||
Genetic transformation | Core inbred lines such as Z58, C7-2, Ph6wc, and Ph4cv | 8 to 10 months | At least 10 batches of T1 generation Bar test strip–positive seeds | |
Single-gene knockout | 8 to 10 months | At least 5 batches of T1 generation edited seeds | ||
Multi-gene knockout | 8 to 10 months | At least 5 batches of edited T1 generation seeds | ||
Precision Editing (PE) | 10 to 12 months | At least 3 edited T0 lines | ||
Tomato | Genetic transformation | AC, MicroTom, Monymaker, and other tomato varieties | 4 to 5 months | At least 15 T0 generation positive plants |
Single-gene knockout | 5 to 6 months | At least 5 edited T0 lines | ||
Multi-gene knockout | 5 to 6 months | At least 5 edited T0 lines | ||
Precision Editing (PE) | 5 to 6 months | At least 3 edited T0 lines | ||
Lettuce | Genetic transformation | Green Butterfly, Rosa Verde, Da Su Sheng, and other lettuce varieties | 4 to 5 months | At least 15 positive T0 plants |
Single-gene knockout | 5 to 6 months | At least 5 edited T0 lines | ||
Multi-gene knockout | 5 to 6 months | At least 5 edited T0 lines | ||
Precision Editing (PE) | 5 to 6 months | At least 3 edited T0 lines | ||
Tobacco | Genetic transformation | Nicotiana benthamiana | 5 to 6 months | At least 15 positive T0 plants |
Single-gene knockout | 5 to 6 months | At least 5 edited T0 lines | ||
Multi-gene knockout | 5 to 6 months | At least 5 edited T0 lines | ||
Precision Editing (PE) | 5 to 6 months | At least 3 edited T0 lines | ||
Arabidopsis thaliana | Genetic transformation | Col-0 | 5 to 6 months | At least 15 positive T1 lines |
Single-gene knockout | 6 to 7 months | At least 5 edited T1 lines | ||
Multi-gene knockout | 6 to 7 months | At least 5 edited T1 lines | ||
Precision Editing (PE) | 6 to 7 months | At least 3 edited T1 lines | ||
Solanum tuberosum | overexpression | Desiree | 4 to 6 months | At least 5 T0 transgenic lines with positive seedlings |
single-gene knockout | 4 to 6 months | At least 3 independent T0 genome-edited lines |
Sample Submission Requirements
Types | Sample submission standards | Transport conditions |
The sequence needs to be synthesized | None | None |
Constructed plasmid Intermediate vector plasmid | Concentration >100 ng/μl, volume >20 μl; vector sequence and antibiotic resistance information provided; no contamination | Ice pack |
Bacterial culture containing the constructed plasmid Bacterial culture containing the intermediate vector plasmid | Volume >500 μl; vector sequence and antibiotic resistance information provided; no contamination | Dry ice: 5 kg for 1 day, 10–20 kg for 2–3 days, 20–30 kg for 3–5 days. |
Bacterial colonies on agar plate | No contamination | Room temperature |
Seeds (uncommon variety) | 200+ seeds | Room temperature |
Case Result
Disclaimer: All products and services are intended for research use only. Not for diagnostic or therapeutic applications.
Services Workflow

Online Consultation
01

Solution Matching
02

Service Contract
03

One-Stop-Services
04

Project Report
05
Related Products
Product Inquiry

Contact Us

Tel: +86 025-85205672

Email: info@pronetbio.com

Address: Building 3C, Nanjing Xianlin Zhigu,
Qixia District, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China, 210033

Need more info?
Let's connect!