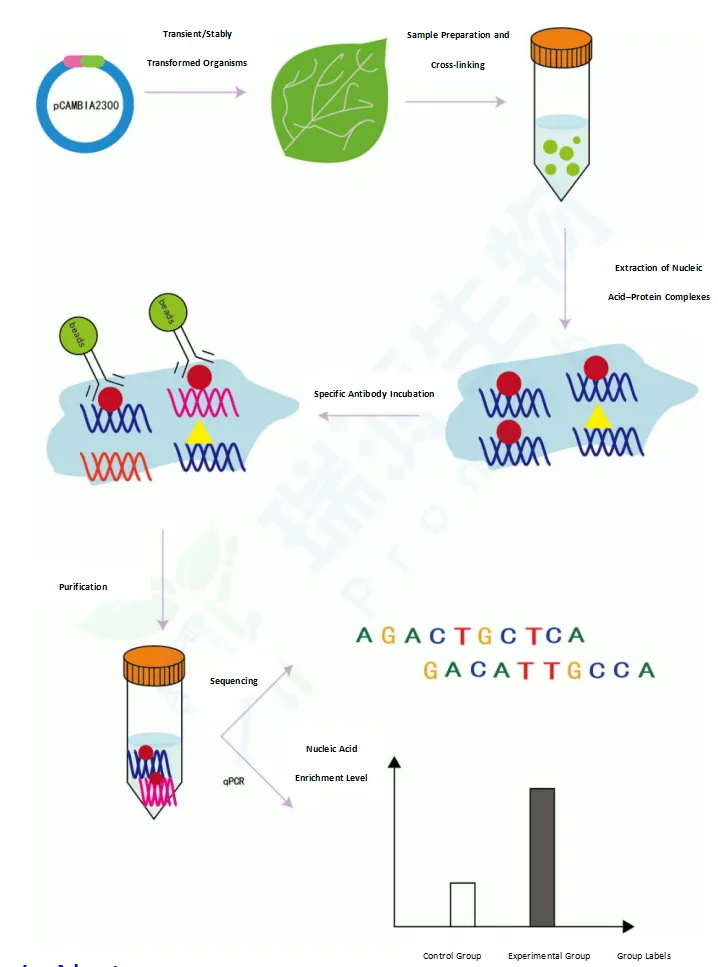
Co-Immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) Services
Co-Immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) Service for Protein-Protein Interaction Validation in Plants and Mammalian Cells
Co-Immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) is a widely used technique for studying protein-protein interactions, enabling the specific enrichment of a target protein along with its interacting partners or protein complexes. Co-IP uses antibodies specific to the protein of interest to perform immunoprecipitation, allowing co-precipitation of proteins bound to the target. The resulting antibody–target protein complexes can then be analyzed by SDS-PAGE, Western blotting, or mass spectrometry. Since cells are lysed under non-denaturing conditions, protein-protein interactions inside the cell are preserved.
At ProNet Biotech, we offer Co-IP services using transient expression systems in both plant and mammalian cells. Combined with Western blot or mass spectrometry detection, our Co-IP platform is well-suited for validating protein interactions discovered through other methods, such as yeast two-hybrid (Y2H) or GST pull-down assays.
Technical Principle
Based on the affinity between specific antibodies (or other binding reagents) and the target protein, the Co-IP technique uses antibodies to immunoprecipitate the protein of interest. Any candidate proteins bound to the target protein are co-precipitated. SDS-PAGE and Western blotting are used to detect whether the candidate protein is present, thereby verifying the protein-protein interaction.
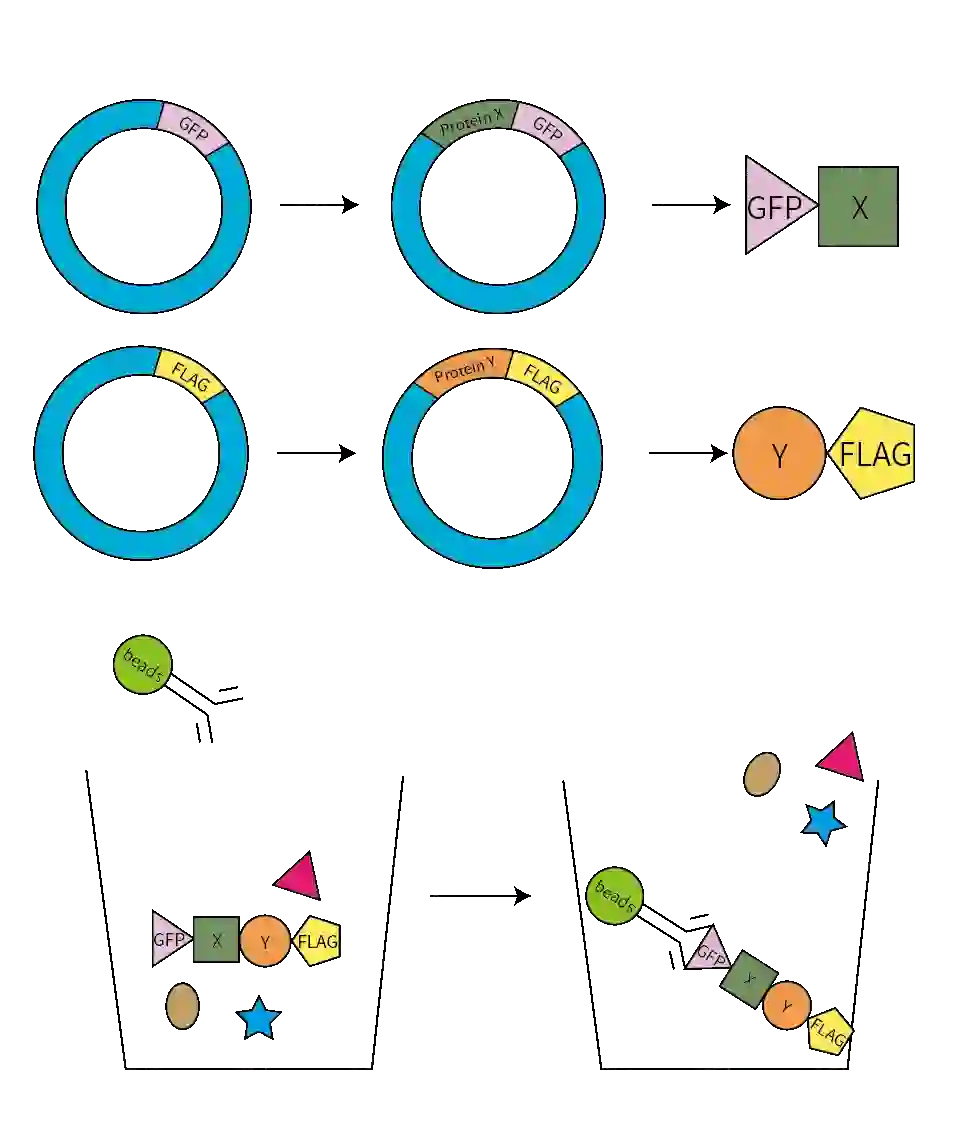
Technical Advantages
1. Every step is strictly monitored, starting from cell transfection.
2. Co-IP can be used not only to validate known protein-protein interactions, but also to discover previously unidentified proteins that interact with the target protein.
3. It enables the detection of interactions occurring under near-physiological conditions and supports further validation through multiple complementary protein interaction assays.
4. Combined with bioinformatics analysis, Co-IP helps predict protein function and uncover the biological significance of protein interactions.
Co-IP Suitable Applications
· Protein Interaction Detection: Co-IP is ideal for determining whether two target proteins interact within living cells.
· Protein Complex Isolation: This technique is suitable for isolating protein complexes that interact in their natural state, providing insights into the physiological roles of these complexes.
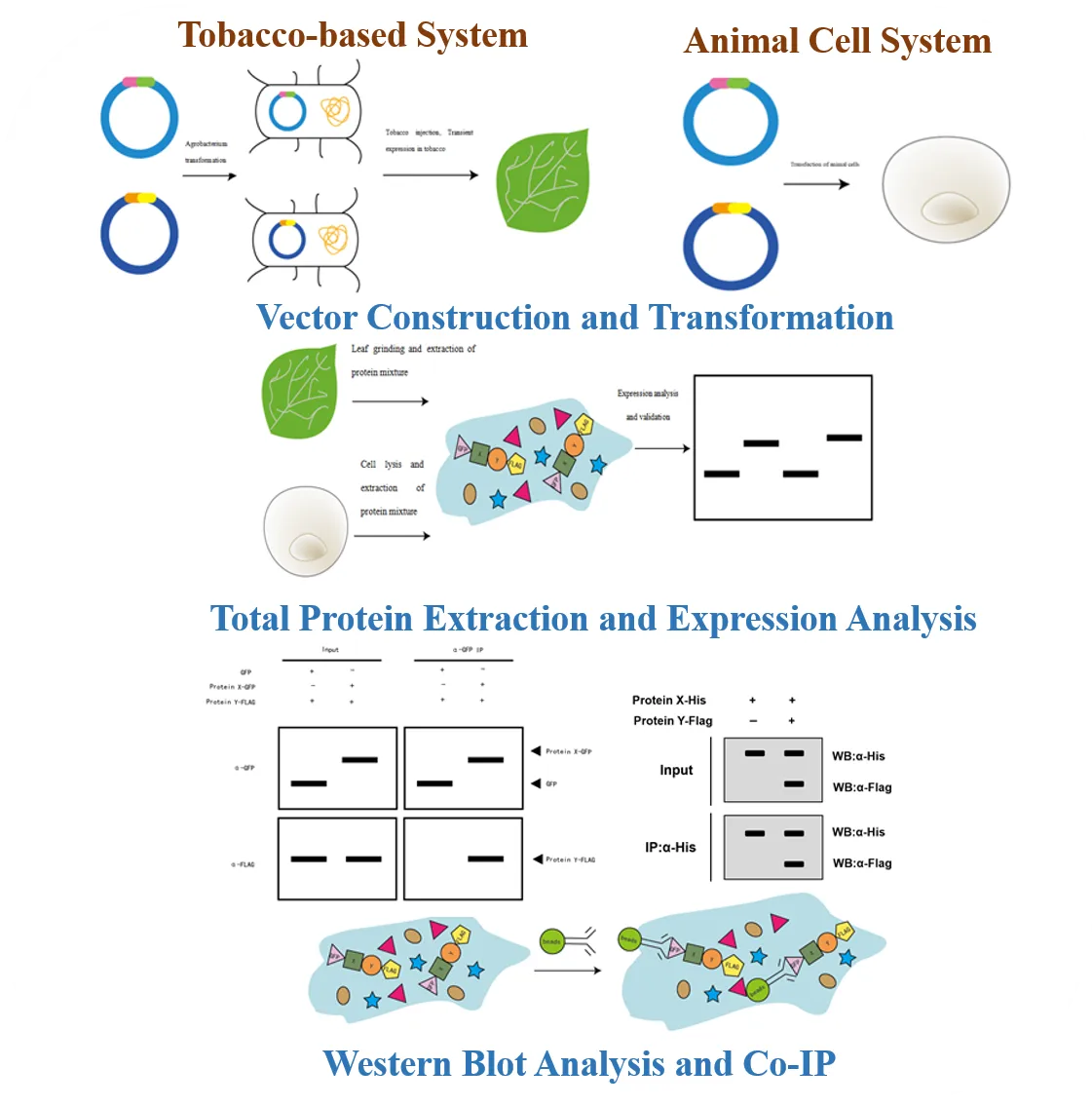
Co-IP Workflow
1. Vector Construction and Transformation
2. Total Protein Extraction and Expression Analysis
3. Western Blot Analysis
4. Co-Immunoprecipitation (Co-IP)
Sample Requirements
Sample Type | Requirement | Shipping |
|---|---|---|
| Sequence for Sythesis | / | / |
Plasmid | >2 µg, with vector map and resistance info | Ice pack |
Bacterial Colonies | >500 µL, sterile & labeled | RT |
Tobacco Leaves | ≥3 infiltrated leaves | Dry ice |
Total Protein Lysate | >500 µL | Dry ice |
Antibody (IP grade) | >30 µL | Dry ice |
Transfected Mammalian Cells | ~3×10⁷ cells (~3×10 cm dishes) | Dry ice |
Cell Lysate with Bait/Prey | >5 mL | Dry ice |
Service Workflow and Deliverables
Tobacco-based System Service Details
Service Content | Working Days | Deliverables |
|---|---|---|
Vector construction 1.Gene optimization and synthesis 2.Subcloning into plant expression vector | 15 | 1. Gene synthesis report 2. Sequencing verification report 3. Plant expression plasmid (Optional) 4. E. coli DH5a/TOP10 with expression plasmids (Optional) |
Plant Transient Expression Analysis 1. Agrobacterium transformation 2. Positive clone identification 3. Plant transient expression 4. Total protein extraction 5. Expression analysis and validation (Western Blot, WB) | 10 | 1. Expression analysis results |
| Co-IP 1. Immunoprecipitation 2. Western Blot validation | 7 | 1. Raw data and result images 2. Standard experimental report (including procedures and procedures) |
Mammalian Cells System Service Details
Service Content | Working Days | Deliverables |
Vector construction 1. Gene optimization and synthesis 2. Subcloning into plant expression vector | 15 | 1. Gene synthesis report 2. Sequencing verification report 3. Animal expression plasmid (Optional) |
Animal Transient Expression Analysis 1.Cell passaging and plating 2.Cell transfection 3.Transient expression 4.Preparation of animal cell lysate 5.Protein extraction 6.Expression analysis and validation (WB) | 10 | Expression analysis results |
Co-IP 1.Immunoprecipitation 2.Western Blot validation | 7 | 1. Raw data and result images 2. Standard experimental report (including procedures and procedures) |
Protein Interaction Experimental Relationships
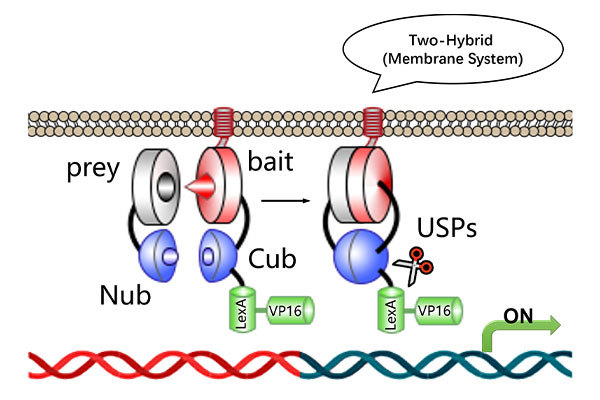
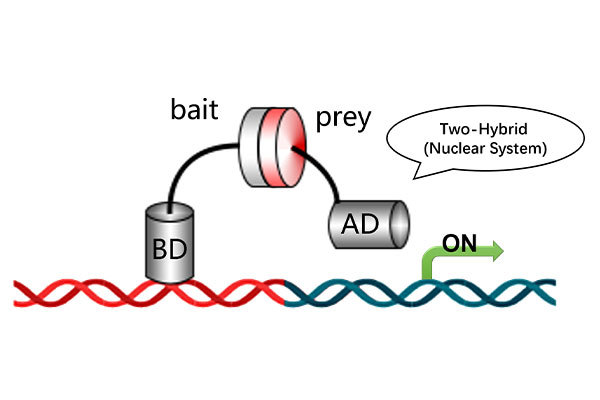
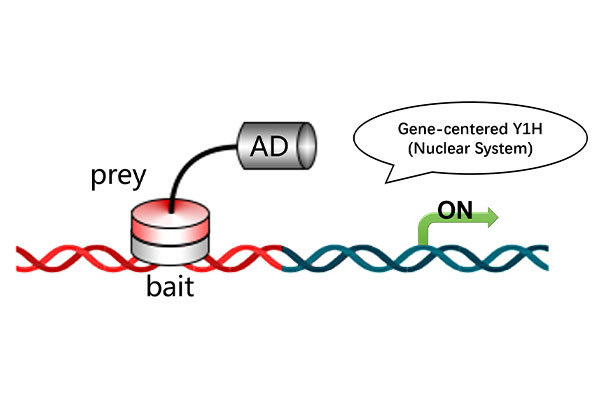
Co-IP is a primary method for detecting protein-protein interactions, but it should be viewed in relation to other experimental techniques like yeast two-hybrid assays and GST pull-down assays.
- Yeast Two-Hybrid: This in vivo experiment helps verify potential protein interactions but can suffer from a higher false-positive rate. Therefore, further validation is often required.
- Co-IP: Co-IP offers a lower false-positive rate and allows the analysis of protein interactions in their natural state. It is particularly effective for isolating naturally interacting protein complexes.
- GST Pull-Down Assay: While Co-IP cannot determine whether the interaction is direct or indirect, the GST pull-down assay can be used to verify direct interactions by isolating the target protein in an in vitro setting.
Together, these methods offer a powerful combination for comprehensive protein interaction validation.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Why do Co-IP and other methods (e.g., BiFC or Y2H) sometimes give different results?
A: If an interaction requires a third protein, it may appear in Co-IP but not in other binary systems like GST pull-down.
Q: What is the difference between IP and Co-IP?
A: Immunoprecipitation (IP) is used to isolate a single target protein using a specific antibody and is primarily considered a protein purification method. Co-Immunoprecipitation (Co-IP), on the other hand, is mainly used to detect interactions between proteins, making it a common technique in protein interaction studies.
Case Studies
High Transformation Efficiency: We consistently achieve high transformation efficiency, ensuring reliable and reproducible results.
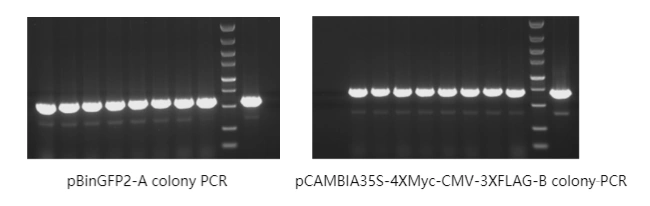
Authentic Data and High-Quality Images: Results include control groups, real data, and aesthetically pleasing images that clearly demonstrate protein interactions.
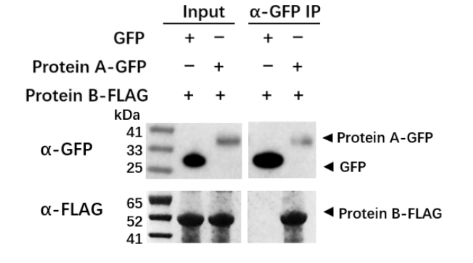
Why Choose ProNet Biotech?
Expertise: Dedicated molecular interaction team with 10+ years of experience.
One-stop services: Data-rich reporting: High-resolution images + standardized documentation.
Data-rich reporting: High-resolution images + standardized documentation.
Global support: Fast communication, customizable workflows, and technical guidance.
Get in Touch
Ready to explore protein interactions in their native cellular context? Contact us today to learn how our Co-IP services can support your next discovery.
Services Workflow

Online Consultation
01

Solution Matching
02

Service Contract
03

One-Stop-Services
04

Project Report
05
Related Products
Product Inquiry